‘I can’t believe I’m still here, either.’ Evan El-Amin/Shutterstock
‘I can’t believe I’m still here, either.’ Evan El-Amin/Shutterstock
Britain recently elected a prime minister who unlawfully shut down parliament to escape democratic scrutiny and who tells blatant falsehoods whenever it suits him. Boris Johnson casually denies the presence of media in front of TV cameras and he denies core elements of his Brexit deal, such as the need for customs checks between Britain and Northern Ireland.
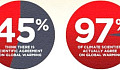
In 2016, US voters faced a choice between a presidential candidate whose campaign statements were accurate 75% of the time and another whose claims were false 70% of the time, according to one factchecking outlet. Americans chose Donald Trump, who has made more than 13,000 false or misleading claims since assuming office.
Trump’s approval ratings have remained largely stable for two years and 77% of Republicans consider him to be honest. Johnson was elected by a landslide and more than half the British public was unconcerned by his shutting down parliament.
How is this possible? How can lying demagogues find traction in societies with proud histories of democracy and empiricism?
Are people insensitive to falsehoods? Do they not know whether things are true or false? Do people no longer care about truth?
The answers are nuanced and rest on the distinction between our conventional understanding of honesty and the notion of “authenticity”. The main element of honesty is factual accuracy whereas the main element of authenticity is an alignment between the public and private persona of a politician.
Research by my team has shown that American voters — including Trump supporters — are responsive to corrections of Trump’s falsehoods. That is, when people learn that a specific claim is false, they reduce their belief in that claim. However, in our results, there was no association between updating of beliefs and feelings towards Trump among his supporters. That is, support remained stable no matter how much people realised that Trump’s statements were inaccurate.
Voters may therefore understand perfectly well that a politician is lying, and they may discount falsehoods when they are pointed out. But the same voters seemingly tolerate being lied to without holding it against their favoured candidate. This disconnect between perceived accuracy and support for a politician has now been shown repeatedly by our team and also by other researchers using a different methodology.
But it does not follow that people have given up on truth and honesty in politics altogether.
Research led by Oliver Hahl of Carnegie Mellon University has identified the specific circumstances in which people accept politicians who lie. It is only when people feel disenfranchised and excluded from a political system that they accept lies from a politician who claims to be a champion of the “people” against the “establishment” or “elite”. Under those specific circumstances, flagrant violations of behaviour that is championed by this elite – such as honesty or fairness — can become a signal that a politician is an authentic champion of the “people” against the “establishment”.
For populist politicians, such as Trump and Johnson, who explicitly pit a mythical people against an equally mythical elite, blatant disregard for facts only underscores their authenticity in the eyes of supporters.
No amount of factchecking will reduce the appeal of Trump, Johnson, Duterte, Bolsonaro or any other populist demagogue around the world.
To defang demagogues, and to make lying unacceptable again, requires that voters regain trust in the political system. The research by Hahl and his colleagues also showed that when people consider a political system to be legitimate and fair, they reject politicians who tell untruths and they resent being lied to. So the key to moving on involves pursuing politics that reduce the appeal of populist demagogues and that create incentives for politicians to be more honest.
There is no quick and easy recipe for this process. But it is clear that we need to have a political conversation about income inequality. In 2015, two dozen hedge fund managers made more money than all the kindergarten teachers in the US combined, and billionaires now pay a lower tax rate than the rest of us. It is unsurprising that inequality has been identified as one of the variables that has compromised the legitimacy of democracy in the eyes of so many people.
Johnson refused to look at the snapshot of a little boy with pneumonia who was forced to sleep on a hospital floor. Once that has become unacceptable, and once sick children find a bed in hospital, Johnson’s falsehoods will also no longer find traction.
Another way is possible
It is encouraging to note that in other countries with different political structures and policies, voters do not tolerate politicians’ lies. Research by my team conducted in Australia has shown that Australian voters reduce their endorsement of politicians if they are revealed to be dishonest.
Using a methodology that exactly paralleled our study with American voters, we found that, unlike in the US, corrections of Australian politicians’ falsehoods made participants much less inclined to support those candidates. This effect occurred irrespective of partisanship, meaning voters were intolerant of lies even if they came from their own side of politics.
In Australia, voting is mandatory and preferential. Everyone must vote or risk being fined, and voters rank their preferences among all parties. These measures help contain political polarisation, underscoring how the design of a political system can determine a country’s welfare.
About The Author
Stephan Lewandowsky, Chair of Cognitive Psychology, University of Bristol
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Books Improving Attitude and Behavior from Amazon's Best Sellers list
"Atomic Habits: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad Ones"
by James Clear
In this book, James Clear presents a comprehensive guide to building good habits and breaking bad ones. The book includes practical advice and strategies for creating lasting behavior change, based on the latest research in psychology and neuroscience.
Click for more info or to order
"Unf*ck Your Brain: Using Science to Get Over Anxiety, Depression, Anger, Freak-Outs, and Triggers"
by Faith G. Harper, PhD, LPC-S, ACS, ACN
In this book, Dr. Faith Harper offers a guide to understanding and managing common emotional and behavioral issues, including anxiety, depression, and anger. The book includes information on the science behind these issues, as well as practical advice and exercises for coping and healing.
Click for more info or to order
"The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business"
by Charles Duhigg
In this book, Charles Duhigg explores the science of habit formation and how habits impact our lives, both personally and professionally. The book includes stories of individuals and organizations who have successfully changed their habits, as well as practical advice for creating lasting behavior change.
Click for more info or to order
"Tiny Habits: The Small Changes That Change Everything"
by BJ Fogg
In this book, BJ Fogg presents a guide to creating lasting behavior change through small, incremental habits. The book includes practical advice and strategies for identifying and implementing tiny habits that can lead to big changes over time.
Click for more info or to order
"The 5 AM Club: Own Your Morning, Elevate Your Life"
by Robin Sharma
In this book, Robin Sharma presents a guide to maximizing your productivity and potential by starting your day early. The book includes practical advice and strategies for creating a morning routine that supports your goals and values, as well as inspiring stories of individuals who have transformed their lives through early rising.
s